《Poly Bridge》全關(guān)卡新手指南圖文攻略
5 -Tips!
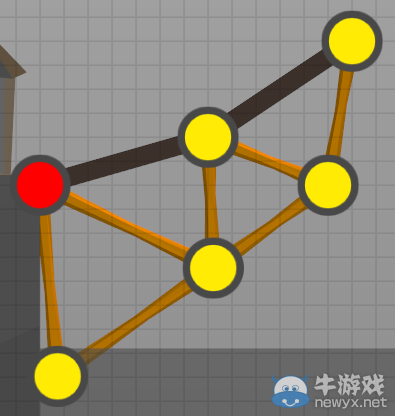
5.1 - StaticJoints靜態(tài)節(jié)點
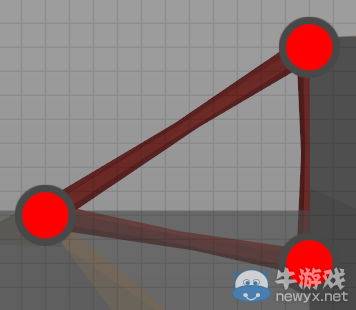
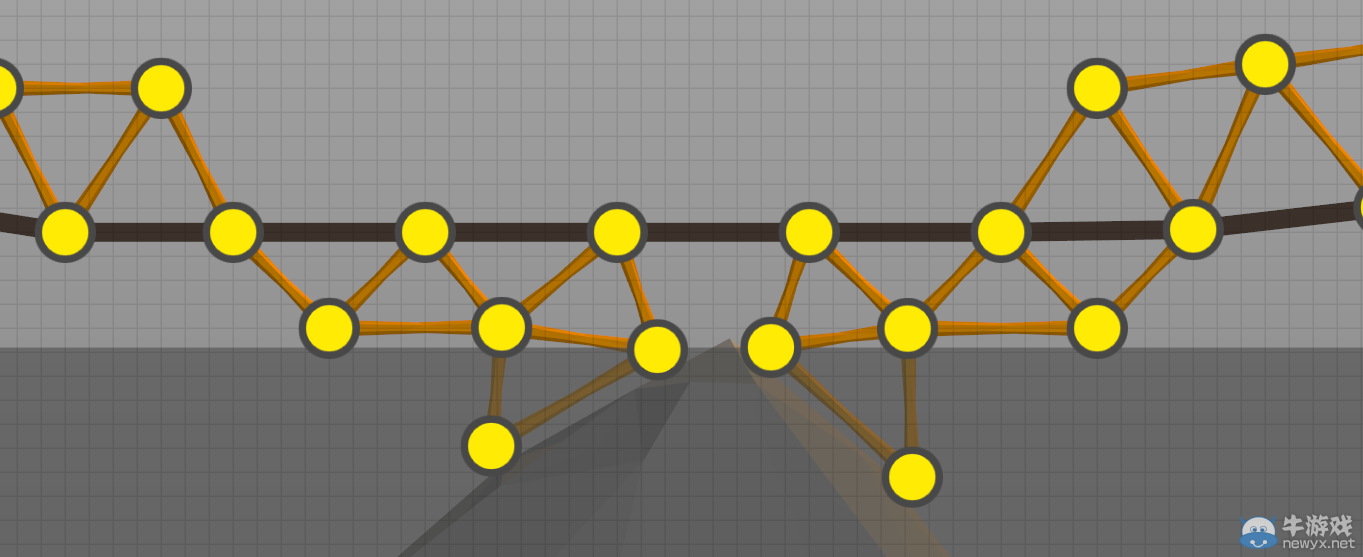
Red static joints are points to distribute the load ofthe structure and vehicles. As they are immovable, connecting two static jointsdirectly to each other has no effect.
紅色靜態(tài)節(jié)點可以分配來自結(jié)構(gòu)和車輛的負載。因為它們是不動的,所以直接連接兩個靜態(tài)節(jié)點,并沒有什么卵用。
靜態(tài)節(jié)點
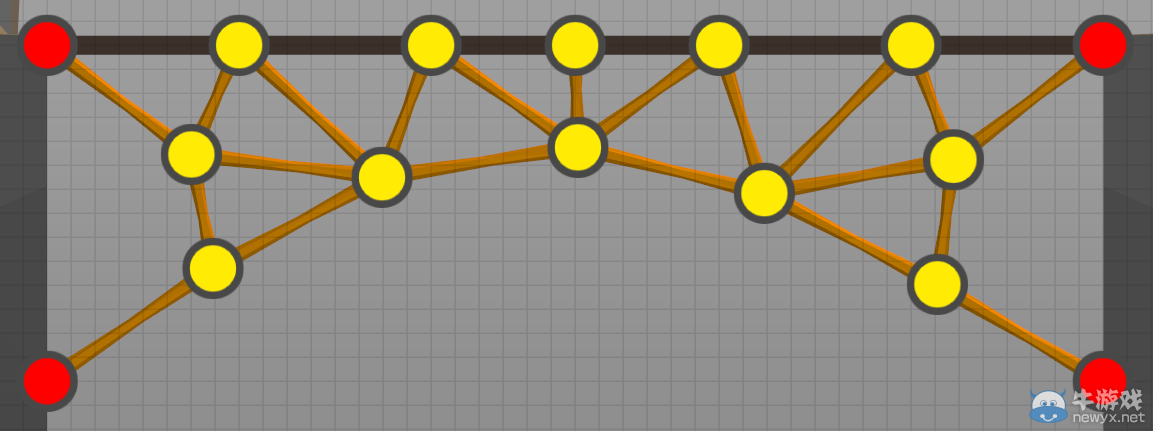
5.2 - Triangles三角頭
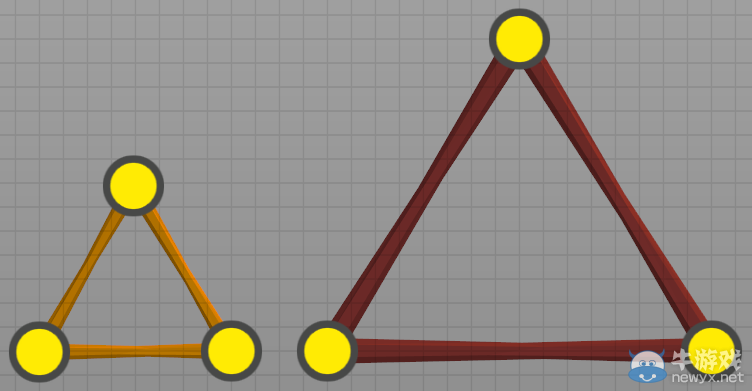
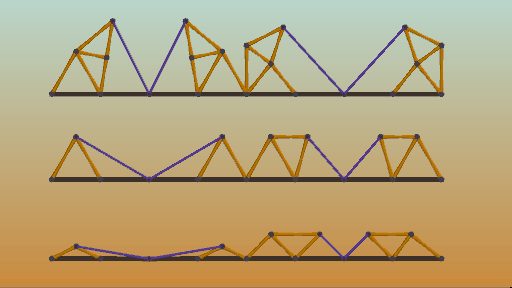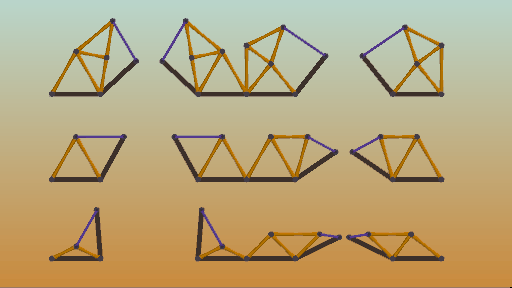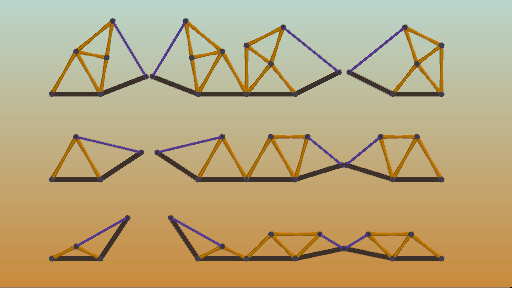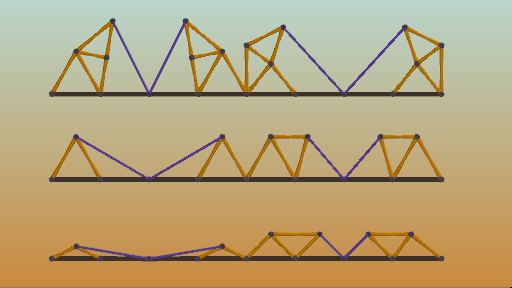
Triangles are your friend! Triangles are one of the strongest shapes, allowing loads tobe distributed throughout a structure without collapsing. Equilateral triangles, triangles with all sides the same length, are especially strong.
三角頭非常強,堪稱陸地上最強的男人,而等邊三角頭也就是究極體三角頭簡直是宇宙最強。
三角結(jié)構(gòu)
(三角形結(jié)構(gòu)非常友好,是結(jié)構(gòu)最強的形狀之一,三角形使負荷分布于整體結(jié)構(gòu),可防止結(jié)構(gòu)塌陷,而等邊三角形則強度更高。)
5.3 - Split Joints分離節(jié)點
Split joints allow you to make planned joint breaks for use with hydraulics. Ensure both sides of the split joint are supported independently.
使用液壓工具時需要先設(shè)置分離節(jié)點,同時要確保分離節(jié)點的兩端有獨立支承。
5.4 - Pivot Points樞紐節(jié)點
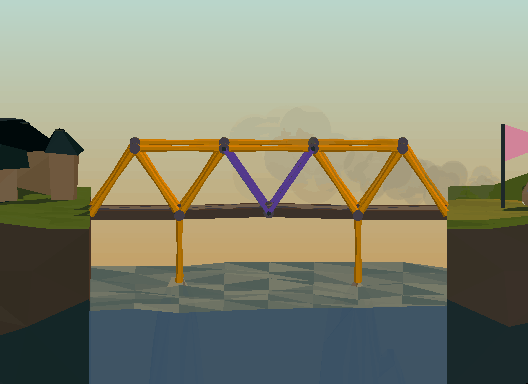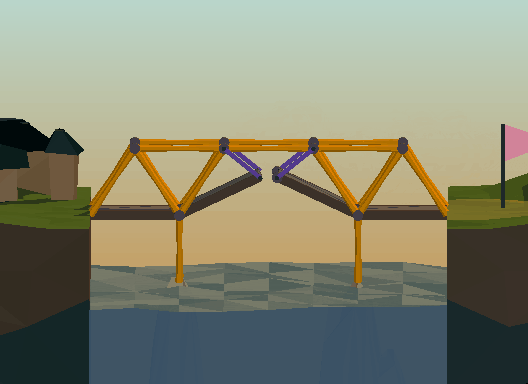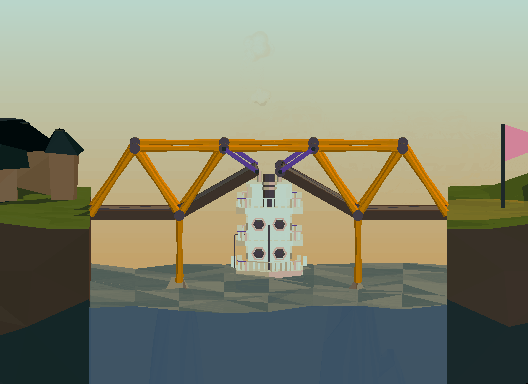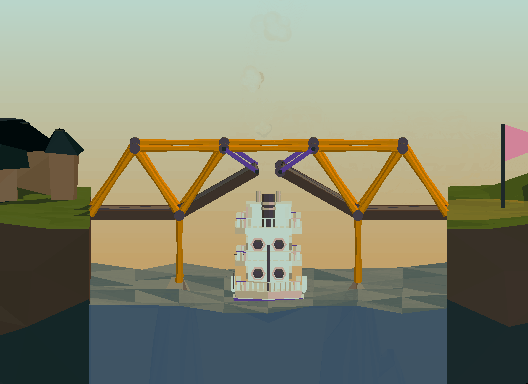
Pivot points can make or break your bridge, literally. Two lengths of material create a pivot point at their joint and can greatly weaken a structure, or be used in a drawbridge.
樞紐節(jié)點既可以造橋,也可能斷橋。因為樞紐節(jié)點會大大降低結(jié)構(gòu)強度,但是吊橋就需要用的樞紐節(jié)點。
動態(tài)示意圖
動態(tài)示意圖
動態(tài)示意圖
5.5 - Arches and Parabolas 拱結(jié)構(gòu)與拋物線型結(jié)構(gòu)
Anarch or parabola is a very strong shape that distributes a load evenly across a structure.
拱結(jié)構(gòu)與拋物線型結(jié)構(gòu)能使負荷均勻分布。(能節(jié)省材料、提高剛度、跨越較大空間)
拱結(jié)構(gòu)示意圖
5.6 - Terrain地形
Use the terrain to your advantage. Terrain, like static joints, is immovable and can be used to rest your structures upon or against.
因地制宜,利用地形作為靜態(tài)節(jié)點。如下圖,你可以利用地形來支撐你的結(jié)構(gòu)。
支撐點示意圖
不同形狀支撐點
5.7 - Detecting Weak Points 找出薄弱環(huán)節(jié)
There are a few ways you can detect weak points in your structure. Turning the stress view on allows you to see the live load on your structure during simulation.You can adjust the speed of the simulation with the slider at the top of your screen. In the replay viewer you can adjust the sliders to see a frame-by-frame view of the action. See 7- Replays for more info.
你可以通過幾種方式找出結(jié)構(gòu)的薄弱環(huán)節(jié)。通過運動仿真的應力視圖你可以看到活載荷,屏幕上方還可以調(diào)節(jié)運行速度。重放錄像的時候你還可以手動調(diào)節(jié)進度條滑塊。
手動調(diào)節(jié)進度條
5.8 - Drawbridges 吊索橋
This illustrates how the original angle(left) and length(right) of Hydraulics change the final position of roads.
下圖顯示了如何通過液壓工具可以改變吊橋的角度(左圖)和長度(右圖)
各種吊橋示意圖
6 -Suspension懸索橋
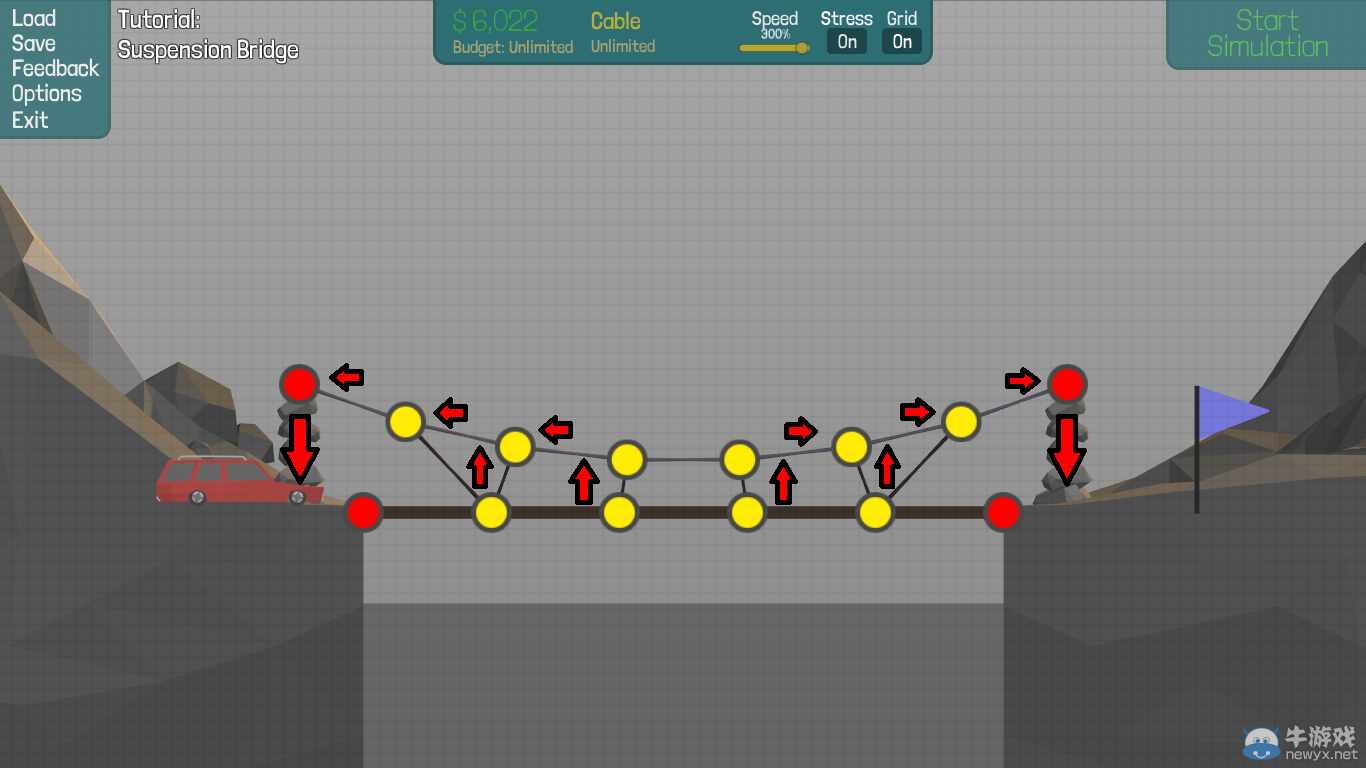
Without getting too specific or technical, a suspension bridge primarily works by placing the load of the structure upon pillars, compressing them downwards.While tricky to work with, suspension bridges can span large distances for much cheaper than steel.
Hint: You don’t have to connect all joints on the suspension, just use what youneed.
無需具體結(jié)構(gòu)或技術(shù),懸索橋?qū)⒇摵啥嫁D(zhuǎn)移到立柱上。懸索橋可以跨越很大的距離,成本也比鋼材結(jié)構(gòu)要低。
(懸索橋,又名吊橋(suspension bridge)指的是以通過索塔懸掛并錨固于兩岸(或橋兩端)的纜索(或鋼鏈)作為上部結(jié)構(gòu)主要承重構(gòu)件的橋梁。)
懸索橋示意圖
- 本文導航
- 第1頁:目錄/操作/界面/狀態(tài)說明 第2頁:材料屬性/車輛/船舶說明 第3頁:節(jié)點/結(jié)構(gòu)/環(huán)節(jié)/橋型說明 第4頁:第一關(guān):高山牧場 第5頁:第二關(guān):沙漠風暴 第6頁:第三關(guān):雪地漂移 第7頁:第四關(guān):遠古遺跡 第8頁:第五關(guān):80年代樂園 第9頁:第六關(guān):禪境花園
-

《Poly Bridge》全關(guān)卡新手指南圖文攻略
瀏覽量:02016-07-06
-

《Poly bridge》第一關(guān)高山牧場圖文攻略
瀏覽量:02016-07-06
-

《Poly Bridge》設(shè)計關(guān)卡及游戲性試玩心得
瀏覽量:02016-07-06
-

《Poly Bridge》第一關(guān)全關(guān)卡最省錢過關(guān)攻略
瀏覽量:02016-07-06
-

《Poly Bridge》按鍵操作指南
瀏覽量:02016-07-05
-

《Poly Bridge》中文設(shè)置方法
瀏覽量:02016-07-05